A Comparative Study of Explainable AI Models in High-Stakes Decision-Making Systems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.63876/ijss.v1i2.72Keywords:
Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI), High-Stakes Decision-Making, Model Interpretability, SHAP and LIME, Counterfactual Explanations, Responsible AIAbstract
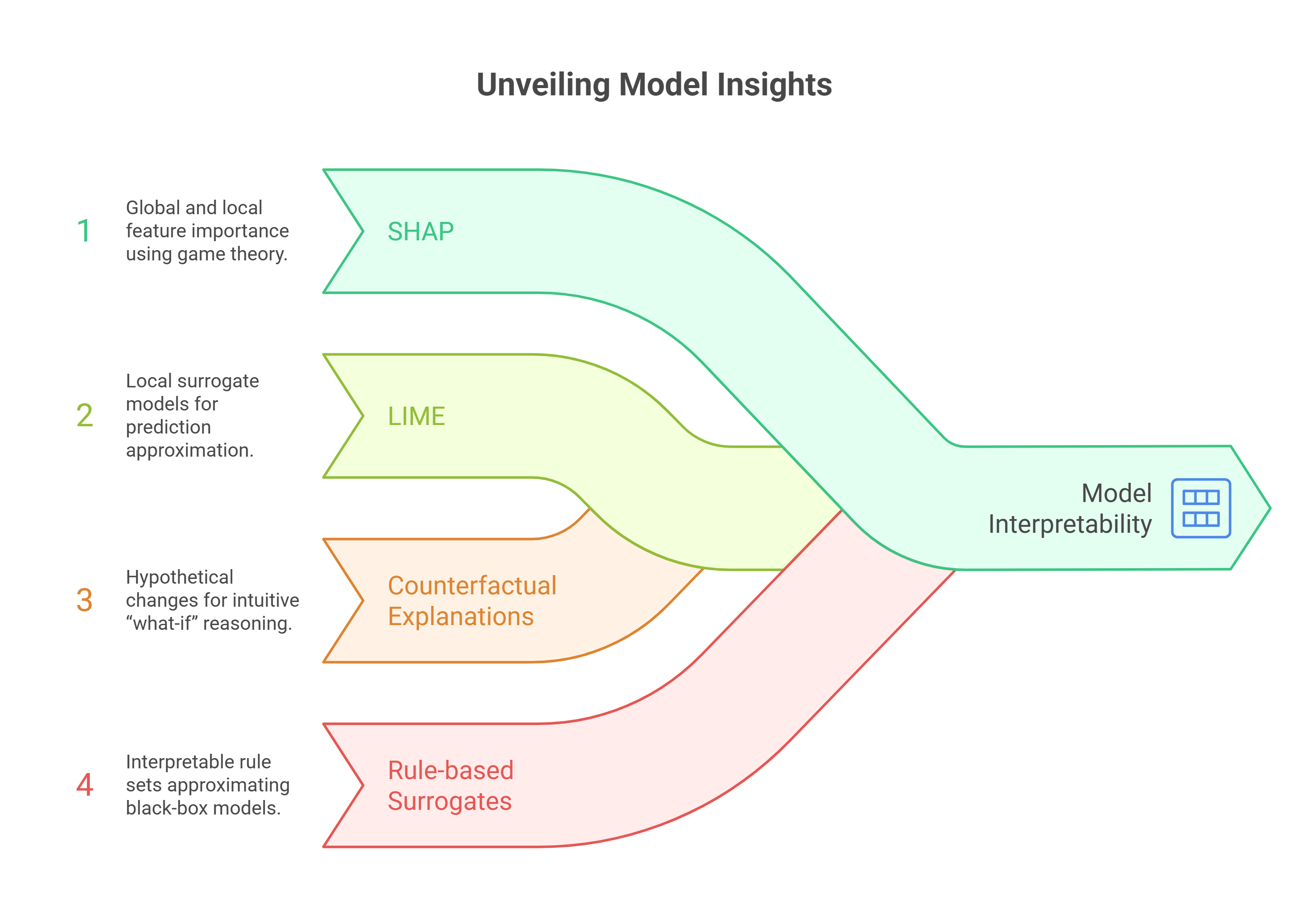
High-stakes decision-making systems such as those used in healthcare, finance, and criminal justicedemand not only high predictive accuracy but also transparency to ensure trust, accountability, and ethical compliance. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) has emerged as a pivotal approach to address the black-box nature of complex machine learning models, offering interpretable insights into model predictions. This study presents a comparative analysis of leading XAI techniques, including SHAP, LIME, Counterfactual Explanations, and Rule-based Surrogates, across three real-world high-stakes domains. Using standardized evaluation metrics—fidelity, stability, usability, and computational efficiency—we examine the trade-offs between explanation quality and system performance. The results reveal that while SHAP consistently provides the highest fidelity explanations, it suffers from higher computational costs, whereas LIME offers faster, though sometimes less stable, explanations. Counterfactual methods excel in user interpretability but face challenges in generating plausible scenarios for complex datasets. Our findings highlight that no single XAI method is universally optimal; rather, the selection should align with domain-specific requirements and the criticality of the decisions involved. This comparative study contributes to the discourse on responsible AI deployment by providing actionable insights for practitioners, policymakers, and researchers seeking to integrate XAI into high-stakes environments.
Downloads
References
K. Paranjape, M. Schinkel, and P. Nanayakkara, “Short Keynote Paper: Mainstreaming Personalized Healthcare-Transforming Healthcare through new era of Artificial Intelligence,” IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Informatics, pp. 1–1, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2020.2970807.
I. Ahmed, G. Jeon, and F. Piccialli, “From Artificial Intelligence to Explainable Artificial Intelligence in Industry 4.0: A Survey on What, How, and Where,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Informatics, vol. 18, no. 8, pp. 5031–5042, Aug. 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2022.3146552.
Saluky, S. H. Supangkat, and F. F. Lubis, “Moving Image Interpretation Models to Support City Analysis,” in 2018 International Conference on ICT for Smart Society (ICISS), IEEE, Oct. 2018, pp. 1–5. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTSS.2018.8550012.
S. Pal, Tanushka, K. Jha, and D. Sharma, “Blockchain-Enhanced AI Diagnostics in Healthcare,” in 2024 International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Innovation for Sustainability (EmergIN), IEEE, Dec. 2024, pp. 258–263. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/EmergIN63207.2024.10961743.
Y. Liu, “Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning based Financial Risk Network Assessment Model,” in 2023 IEEE 12th International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies (CSNT), IEEE, Apr. 2023, pp. 158–163. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CSNT57126.2023.10134653.
P. Kourouklidis, D. Kolovos, J. Noppen, and N. Matragkas, “A Model-Driven Engineering Approach for Monitoring Machine Learning Models,” in 2021 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems Companion (MODELS-C), IEEE, Oct. 2021, pp. 160–164. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/MODELS-C53483.2021.00028.
Y. Yuan, L. Mou, and X. Lu, “Scene Recognition by Manifold Regularized Deep Learning Architecture,” IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst., vol. 26, no. 10, pp. 2222–2233, Oct. 2015, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2359471.
J. P. Zubrod, N. Galic, M. Vaugeois, and D. A. Dreier, “Bio-QSARs 2.0: Unlocking a new level of predictive power for machine learning-based ecotoxicity predictions by exploiting chemical and biological information,” Environ. Int., vol. 186, p. 108607, Apr. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2024.108607.
A. Bujold, X. Parent-Rocheleau, and M.-C. Gaudet, “Opacity behind the wheel: The relationship between transparency of algorithmic management, justice perception, and intention to quit among truck drivers,” Comput. Hum. Behav. Reports, vol. 8, p. 100245, Dec. 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chbr.2022.100245.
I. Fernandez, C. Aceta, E. Gilabert, and I. Esnaola-Gonzalez, “FIDES: An ontology-based approach for making machine learning systems accountable,” J. Web Semant., vol. 79, p. 100808, Dec. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.websem.2023.100808.
B. Covolan and J. L. Bender, “Product Safety - the Importance and Impact of Ethical Compliance Practices,” in 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Product Compliance Engineering (ISPCE), IEEE, Sep. 2022, pp. 1–4. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ISPCE54918.2022.10017194.
IEEE, “IEEE Draft Guide for an Architectural Framework for Explainable Artificial Intelligence,” 2023.
L. Valina, B. Teixeira, A. Reis, Z. Vale, and T. Pinto, “Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Deep Synthetic Data Generation Models,” in 2024 IEEE Conference on Artificial Intelligence (CAI), IEEE, Jun. 2024, pp. 555–556. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CAI59869.2024.00109.
E. N. Volkov and A. N. Averkin, “Explainable Artificial Intelligence in Medical Image Analysis: State of the Art and Prospects,” in 2023 XXVI International Conference on Soft Computing and Measurements (SCM), IEEE, May 2023, pp. 134–137. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/SCM58628.2023.10159033.
S. M. Gbashi, O. O. Olatunji, P. A. Adedeji, and N. Madushele, “An Explainable AI Approach Using SHapley Additive exPlanations for Feature Selection in Vibration-Based Fault Diagnostics of Wind Turbine Gearbox,” in 2024 IEEE 5th International Conference on Electro-Computing Technologies for Humanity (NIGERCON), IEEE, Nov. 2024, pp. 1–5. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/NIGERCON62786.2024.10927384.
W. Ge, J. Patino, M. Todisco, and N. Evans, “Explaining Deep Learning Models for Spoofing and Deepfake Detection with Shapley Additive Explanations,” in ICASSP 2022 - 2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), IEEE, May 2022, pp. 6387–6391. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP43922.2022.9747476.
H. Farhood, M. Saberi, and M. Najafi, “Improving Object Recognition in Crime Scenes via Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations,” in 2021 IEEE 25th International Enterprise Distributed Object Computing Workshop (EDOCW), IEEE, Oct. 2021, pp. 90–94. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/EDOCW52865.2021.00037.
N. Barr Kumarakulasinghe, T. Blomberg, J. Liu, A. Saraiva Leao, and P. Papapetrou, “Evaluating Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations on Clinical Machine Learning Classification Models,” in 2020 IEEE 33rd International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), IEEE, Jul. 2020, pp. 7–12. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CBMS49503.2020.00009.
Z. Cheng, Y. Miao, and X. Zhang, “An Uncertainty Network Working Mechanism Analysis Method based on Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations,” in 2022 China Automation Congress (CAC), IEEE, Nov. 2022, pp. 4000–4004. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CAC57257.2022.10055744.
D. Yu, Q. Li, X. Wang, Q. Li, and G. Xu, “Counterfactual Explainable Conversational Recommendation,” IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng., vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 2388–2400, Jun. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2023.3322403.
X. Zhu, D. Wang, W. Pedrycz, and Z. Li, “Fuzzy Rule-Based Local Surrogate Models for Black-Box Model Explanation,” IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., vol. 31, no. 6, pp. 2056–2064, Jun. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2022.3218426.
M. Kamali, K. Ponnambalam, and E. D. Soulis, “Hydrologic model Calibration using Fuzzy TSK surrogate model,” in NAFIPS 2005 - 2005 Annual Meeting of the North American Fuzzy Information Processing Society, IEEE, pp. 799–803. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/NAFIPS.2005.1548642.
T. R. Razak, J. M. Garibaldi, C. Wagner, A. Pourabdollah, and D. Soria, “Toward a Framework for Capturing Interpretability of Hierarchical Fuzzy Systems—A Participatory Design Approach,” IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., vol. 29, no. 5, pp. 1160–1172, May 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2969901.
Haofu Liao and Ping Chen, “Explore a way of improving the computational efficiency of the block in SCILAB,” in 2011 IEEE International Workshop on Open-source Software for Scientific Computation, IEEE, Oct. 2011, pp. 13–16. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/OSSC.2011.6184686.
Z. Jalil and A. A. Shahid, “Is Non Technical Person a Better Software Project Manager?,” in 2008 International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering, IEEE, 2008, pp. 1–5. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CSSE.2008.1125.
A. K. Davison, C. Lansley, N. Costen, K. Tan, and M. H. Yap, “SAMM: A Spontaneous Micro-Facial Movement Dataset,” IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput., vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 116–129, Jan. 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TAFFC.2016.2573832.
M. Farkhadov, A. Eliseev, and N. Petukhova, “Explained Artificial Intelligence Helps to Integrate Artificial and Human Intelligence Into Medical Diagnostic Systems: Analytical Review of Publications,” in 2020 IEEE 14th International Conference on Application of Information and Communication Technologies (AICT), IEEE, Oct. 2020, pp. 1–4. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/AICT50176.2020.9368576.
R. C. Fong and A. Vedaldi, “Interpretable Explanations of Black Boxes by Meaningful Perturbation,” in 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), IEEE, Oct. 2017, pp. 3449–3457. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.371.
A. Calvo, S. Escuder, J. Escrig, X. Marrugat, N. Ortiz, and J. Guijarro, “Achieving High-Fidelity Explanations for Risk Exposition Assessment in the Cybersecurity Domain,” in 2023 APWG Symposium on Electronic Crime Research (eCrime), IEEE, Nov. 2023, pp. 1–10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/eCrime61234.2023.10485502.
Y. Liu and H. Gao, “Stability, Scalability, Speedability, and String Stability of Connected Vehicle Systems,” IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst., vol. 52, no. 5, pp. 2819–2832, May 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2021.3054794.
S. Domenech, J. Villar, F. A. Campos, and M. Rivier, “Towards a simplified approach for modeling policymaker’s decisions in the power sector,” in 2017 14th International Conference on the European Energy Market (EEM), IEEE, Jun. 2017, pp. 1–5. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/EEM.2017.7981951.
S. Ruan, S. El-Ashram, Z. Mahmood, R. Mehmood, and W. Ahmad, “Density Peaks Clustering for Complex Datasets,” in 2016 International Conference on Identification, Information and Knowledge in the Internet of Things (IIKI), IEEE, Oct. 2016, pp. 87–92. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IIKI.2016.20.
M. A. I. Mozumder, T. P. T. A., R. I. Sumon, S. M. I. Uddin, A. Athar, and H.-C. Kim, “The Metaverse for Intelligent Healthcare using XAI, Blockchain, and Immersive Technology,” in 2023 IEEE International Conference on Metaverse Computing, Networking and Applications (MetaCom), IEEE, Jun. 2023, pp. 612–616. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/MetaCom57706.2023.00107.
T. A. Roshinta and S. Gábor, “A Comparative Study of LIME and SHAP for Enhancing Trustworthiness and Efficiency in Explainable AI Systems,” in 2024 IEEE International Conference on Computing (ICOCO), IEEE, Dec. 2024, pp. 134–139. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICOCO62848.2024.10928183.
L. N. Reddi, R. L. Boren, G. Degardin, and S. Chintalapati, “Evaluation of a holistic framework for leadership training of engineering students,” in 2022 IEEE IFEES World Engineering Education Forum - Global Engineering Deans Council (WEEF-GEDC), IEEE, Nov. 2022, pp. 1–5. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/WEEF-GEDC54384.2022.9996228.